Additional 4.41% of electricity! DAS Solar’s N-type modules have excellent power generation performance
2023-06-27
The N-type Hainan PV plant project, which installed DAS Solar modules was successfully connected to the grid in the fourth quarter of 2022. After five months of stable operation, actual measurements revealed a 4.41% increase in power generation compared to the same installed capacity of P-type.

Hainan province has a tropical monsoon climate, with an average annual temperature of 24 ℃ and an average annual rainfall of around 1400mm. Hainan province boasts abundant sunlight resources, with an annual total solar irradiation of approximately 1500 kWh/m². These conditions offer favorable prerequisites for the construction of PV projects. The project has an approximate DC-side installed capacity of 100 MW. It incorporates DAS Solar's bifacial double-glass N-type modules and P-type modules, both designed with 28 cells in a series configuration. Each group has 17-18 serial PV modules and connected to a 196 kW string inverter, and a total of 16 inverters are linked to a 3.15 MW capacity transformer. The following is the corresponding power generation data from the same string and power design installation comparison.
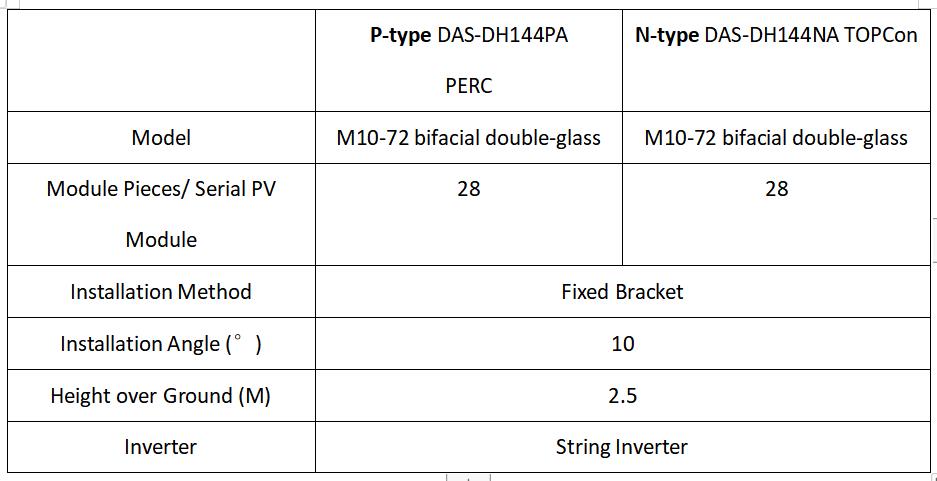
PV plant design parameters
N-type delivering higher profit
The data of power generation was compared from two arrays with identical installation environments: N-type modules (inverter 24-11) and P-type modules (inverter 23-11). Upon analyzing the power generation data from December 2022 to April 2023, it is evident that the N-type modules, with the same installed capacity as the P-type modules, consistently outperformed in terms of power generation. Over the course of five months, an average power generation gain of 4.41% was observed for the N-type modules.
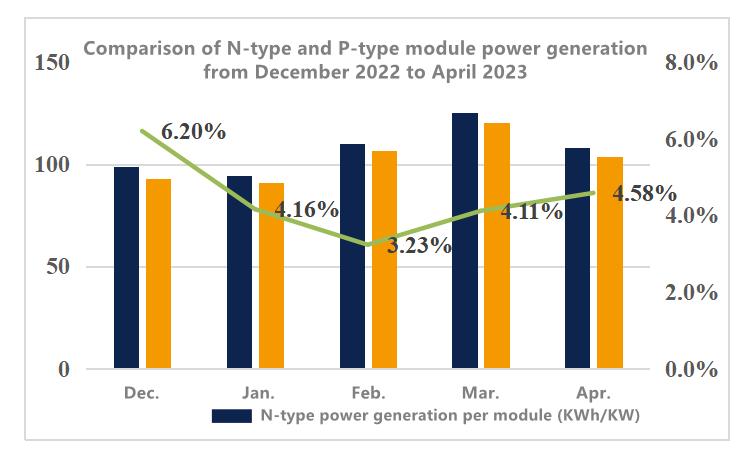
Low power degradation
N-type modules have advantages in degradation. Over a 30-year operational period, N-type modules have lower annual power degradation compared to P-type modules. As the PV plant continues to operate and accumulate more working hours, the power generation gain of N-type modules relative to P-type modules progressively increases. N-type modules experience an initial power degradation of 1% in the first year, followed by an annual degradation rate of 0.4%. In contrast, P-type modules undergo an initial power degradation of 2% in the first year, with an annual degradation rate of 0.45% thereafter. Considering solely the impact of low power degradation, the power generation gain of N-type modules relative to P-type modules grows from 1% in the first year to 2.45% in the 30 years, resulting in an overall increase of 1.73%.
Low-temperature coefficient
The power generation of the modules is correlated with temperature coefficients and operating temperatures. N-type modules have a temperature coefficient of -0.30% /℃, while P-type modules have a temperature coefficient of -0.34%/℃. When comparing the N-type and P-type, the temperature coefficient of N-type modules is 11.76% lower than that of P-type modules. This lower coefficient provides N-type modules with a more pronounced advantage in high-temperature conditions during the summer when module operating temperatures are elevated. Measured data indicates that neighboring N-type modules have an average operating temperature of approximately 2 ℃ lower than P-type modules. N-type has higher conversion efficiency and can convert sunlight into electrical energy. The portion of sunlight converted into heat is reduced, leading to lower module operating temperatures and mitigating power generation losses.

High Bifaciality
N-type modules not only possess high front-side efficiency but also exhibit a substantial increase in back-side power generation compared to P-type. The bifacial N-type modules achieve a bifaciality of 80%, while P-type modules have a bifaciality of 70%. This indicates that the bifaciality of N-type modules is 14.3% higher than that of P-type. Assuming a backside power generation gain of 10% for P-type modules, the backside gain for N-type modules would reach as high as 11.43%, resulting in an approximate 1.4% increase in unit power generation. The N-type modules exhibit superior performance advantages, including low degradation, high-temperature power generation, high bifaciality, and low irradiation power generation. Compared to P-type, which offers a theoretical power generation gain of approximately 3%-5%. Based on the cost difference of $0.07/ W between N-type and P-type modules, the PV plant's Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) is 2.3% lower and is 0.34% higher overall return on investment for the project. As a top-tier brand in N-type technology, DAS Solar is committed to offer exceptional N-type data to deliver stable, reliable, and highly profitable solutions to global customers.






 浙公网安备33080302000236
浙公网安备33080302000236